7.8 KiB
Usage
To open the UI to modify the mappings, look into your applications menu
and search for 'Key Mapper'. You should be prompted for your sudo password
as special permissions are needed to read events from /dev/input/ files.
You can also start it via sudo key-mapper-gtk.
Hitting a key on the device that is selected in the large dropdown on the top should display the key on the bottom of the window, and write it into the selected row (as shown in the screenshots).
For changes to take effect, save the preset first. Otherwise, the daemon won't be able to know about your changes. Afterwards press the "Apply" button.
To change the mapping, you need to use the "Restore Defaults" button, so that the application can read the original keycode. It would otherwise be invisible since the daemon maps it independently of the GUI.
Troubleshooting
If stuff doesn't work, check the output of sudo key-mapper-gtk -d and feel free
to open up an issue here.
Make sure to not post any debug logs that were generated while you entered
private information with your device. Debug logs are quite verbose.
If injecting stops after closing the window, the service is not running.
Try sudo systemctl start key-mapper in a terminal.
If key-mapper or your presets prevents your input device from working at all due to autoload, please try to replug your device, wait 3 seconds and replug it again. No injection should be running anymore.
Combinations
Select the key in your row (click here) and hold a few buttons down.
Releasing them will make your text cursor jump into the mapping column
to type in what you want to map it to.
Combinations involving Ctrl might not work, I think the desktop environment grabs them or something. Combinations with Shift might not work the way you would expect. If it outputs the keycode for a, you are going to get an 'A', because X11 still sees the enabled shift button.
This happens, because all key-mapper does is either forwarding or mapping your keycodes (which is easier said than done), and X11/Wayland has to decide what to do with it. And it decides, that if shift is pressed down, it will capitalize your stuff.
A better option for a key combination would be KP1 + a instead of
LEFTSHIFT + a, because there won't be any side effect. You can disable
KP1 by mapping it to disable, so you won't trigger writing a "1" into
your focused application.
Writing Combinations
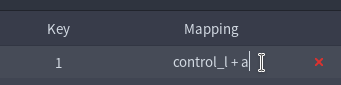
You can write control_l + a as mapping, which will inject those two
keycodes into your system on a single key press. An arbitrary number of
names can be chained using +.
Macros
It is possible to write timed macros into the center column:
k(1).k(2)1, 2r(3, k(a).w(500))a, a, a with 500ms pausem(Control_L, k(a).k(x))CTRL + a, CTRL + xk(1).h(k(2)).k(3)writes 1 2 2 ... 2 2 3 while the key is pressed
Documentation:
rrepeats the execution of the second parameterwwaits in millisecondskwrites a single keystrokemholds a modifier while executing the second parameterhexecutes the parameter as long as the key is pressed down.executes two actions behind each other
Syntax errors are shown in the UI on save. Each k function adds a short
delay of 10ms between key-down, key-up and at the end. See
Configuration Files for more info.
Bear in mind that anti-cheat software might detect macros in games.
Key Names
Check the autocompletion of the GUI for possible values. You can also
obtain a complete list of possiblities using key-mapper-control --key-names.
Examples:
- Alphanumeric
atozand0to9 - Modifiers
Alt_LControl_LControl_RShift_LShift_R - Mouse buttons
BTN_LEFTBTN_RIGHTBTN_MIDDLEBTN_SIDE... - Multimedia keys
KEY_NEXTSONGKEY_PLAYPAUSE...
Gamepads
Joystick movements will be translated to mouse movements, while the second joystick acts as a mouse wheel. You can swap this in the user interface. All buttons, triggers and D-Pads can be mapped to keycodes and macros.
The D-Pad can be mapped to W, A, S, D for example, to run around in games, while the joystick turns the view (depending on the game).
Tested with the XBOX 360 Gamepad. On Ubuntu, gamepads worked better in Wayland than with X11 for me.
Advanced
You usually don't need the stuff described here, you can configure everything via the gui as well.
If you have trouble mapping some keys because the gui loses focus, or if you don't have a graphical user interface, you'll need to edit the configuration files.
Configuration Files
The default configuration is stored at ~/.config/key-mapper/config.json.
The current default configuration as of 0.6.1 looks like, with
an example autoload entry:
{
"autoload": {
"Logitech USB Keyboard": "preset name"
},
"macros": {
"keystroke_sleep_ms": 10
},
"gamepad": {
"joystick": {
"non_linearity": 4,
"pointer_speed": 80,
"left_purpose": "mouse",
"right_purpose": "wheel",
"x_scroll_speed": 2,
"y_scroll_speed": 0.5
}
}
}
preset name refers to ~/.config/key-mapper/presets/device name/preset name.json.
The device name can be found with sudo key-mapper-control --list-devices.
Anything that is relevant to presets can be overwritten in them as well.
Here is an example configuration for preset "a" for the "gamepad" device:
~/.config/key-mapper/presets/gamepad/a.json
{
"macros": {
"keystroke_sleep_ms": 100
},
"mapping": {
"1,315,1+1,16,-1": "1",
"1,307,1": "k(2).k(3)"
}
}
Both need to be valid json files, otherwise the parser refuses to work. This
preset maps the EV_KEY down event with code 307 to a macro and sets the time
between injected events of macros to 100 ms. The other mapping is a key
combination, chained using +.
Note that a complete keystroke consists of two events: down and up. Other
than that, it inherits all configurations from
~/.config/key-mapper/config.json. If config.json is missing some stuff,
it will query the hardcoded default values.
The event codes can be read using evtest. Available names in the mapping
can be listed with key-mapper-control --key-names.
CLI
key-mapper-control
--command requires the service to be running. You can start it via
systemctl start key-mapper or sudo key-mapper-service if it isn't already
running (or without sudo if your user has the appropriate permissions).
Examples:
key-mapper-control --command autoload
# if you are running as root user, provide information about the whereabouts of the key-mapper config:
key-mapper-control --command autoload --config-dir "/home/user/.config/key-mapper/"
sudo key-mapper-control --list-devices
key-mapper-control --command stop --device "Razer Razer Naga Trinity"
# load ~/.config/key-mapper/presets/Razer Razer Naga Trinity/a.json:
key-mapper-control --command start --device "Razer Razer Naga Trinity" --preset "a"
systemctl
Stopping the service will stop all injections until the computer is rebooted.
sudo systemctl stop key-mapper
sudo systemctl start key-mapper
systemctl status key-mapper
Testing your Installation
The following commands can be used to make sure it works:
sudo key-mapper-service &
key-mapper-control --command hello
should print Daemon answered with "hello". And
sudo key-mapper-control --list-devices
should print Found "...", .... If anything looks wrong, feel free to create
an issue.