- Bookmarks and command/directory history functions implemented - Function to edit commandline with $EDITOR - Faster git parser |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| fish_greeting.fish | ||
| fish_prompt.fish | ||
| fish_right_prompt.fish | ||
| README.md | ||
Budspencer theme
A theme for the 70s, makes fish even more powerful. It's equipped with a few nice functions and key bindings to speed up your workflow.
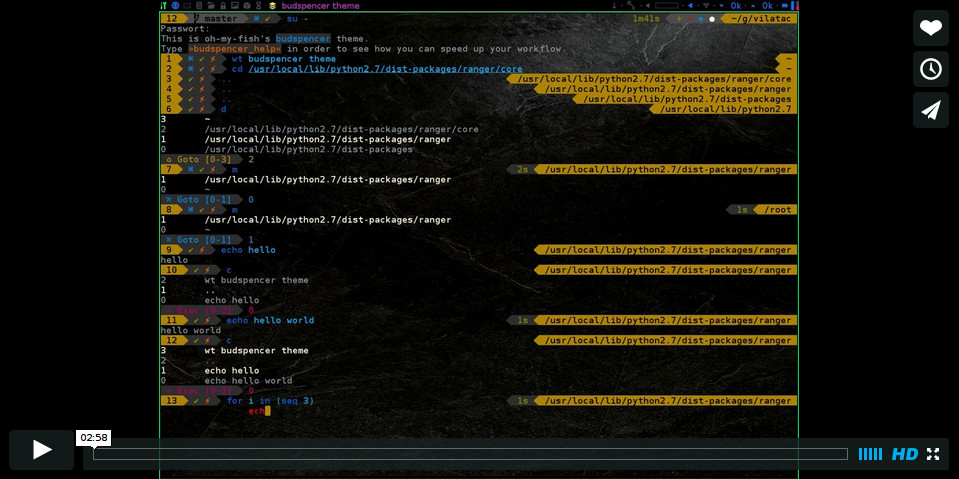
Demonstration video
Requirements
You need an up-to-date fish shell version from github or a nightly build.
Non standard tools:
- xsel
- wmctrl
- git
- taskwarrior (optional)
- remind (optional)
Configuration
General configuration
The theme behaves similar to vim's airline/powerline plugins. Thus, it needs a powerline font. Although it works with emacs mode, it's more powerful with vi mode. In order to enable vi mode, execute:
set -U fish_key_bindings fish_vi_key_bindings
Colors
Redefine $budspencer_colors with the set command in order to change the
colors of the prompt.
Example:
set budspencer_colors 000000 333333 666666 ffffff ffff00 ff6600 ff0000 ff0033 3300ff 0000ff 00ffff
00ff00
will result in a prompt like this:

Two color schemes for bright and dark environments are predefined. You can
enable them with day and night, respectively.
Command history
Commands that shouldn't appear in the command history are defined by a universal
list $budspencer_nocmdhist. Default:
set -U budspencer_nocmdhist c d ll ls m s
Disable/reenable greeting
Disable:
set -U budspencer_nogreeting
Reenable:
set -e budspencer_nogreeting
Outer prompt segments
- Vi mode is indicated by color of outer segments, cursor color also changes
if terminal supports it:
- blue: NORMAL mode
- yellow: INSERT mode
- magenta: VISUAL mode
Left prompt segments
- Prompt line number
- Git repository information
- Status symbols
- ✻: keep track of this shell session, can be toggled with
#to show the number of the session within the sessions list - ⌘: present working directory is in bookmark list, can be toggled with
#to show the number of the bookmark - V: vi is parent process
- R: ranger is parent process
- ⚙: there are background jobs, can be toggled with
#to show the amount of background jobs - : no write permissions in present working directory
- ⚔: there are tasks scheduled due today, can be toggled with
#to show the amount of tasks - ⚑: there are appointments for today, can be toggled with
#to show the amount of appointments - ✔: last command succeeded, can be toggled with
#to show the status value - ✘: last command failed, can be toggled with
#to show the status value - ⚡: superuser indicator
- ✻: keep track of this shell session, can be toggled with
- Present working directory
Right prompt segments
- Last command's duration time
- Git status symbols:
- ↑: git repository is ahead origin
- ↓: git repository is behind origin
- +: changes have been added to git index
- –: files have been deleted in work tree
- ✱: files have been modified in work tree
- →: files have been renamed in git index
- ═: there are unmerged commits
- ●: there are untracked (new) files
- ✭: there are stashed commits
Toggle prompt segments
The following shortcuts need vi-mode:
-
Style of "present working directory"-segment can be toggled in NORMAL and in VISUAL mode with space bar
- styles implemented:
short(shows username, short hostname and truncated path; recommended in most cases)long(shows username, full hostname and full path; useful for copy-paste in ssh connections)none(shows nothing except small delimiter; useful for small terminals)- If prompt is toggled with
#, the IP address is shown instead of the hostname.
- configurable by universal list
$budspencer_pwdstyle(if not set, defaults toshort long none); note that changes to$budspencer_pwdstylekeep persistant as it's a universal variable.
- styles implemented:
-
Style of symbols can be toggled in NORMAL and in VISUAL mode with
#- styles implemented:
symbols(shows status symbols)numbers(shows numbers instead of symbols in left prompt as well as amount of changes in right git prompt)
- styles implemented:
Quickly navigate in history of working directories
The function d shows the history as enumerated list. Unlike fish's builtin
dirh, d does not show any duplicates. Enter a number to jump to a directory
within the list.
The following shortcuts need vi-mode:
- Press
Hin NORMAL mode to change present working directory to previous working directory in history. - Press
Lin NORMAL mode to change present working directory to next working directory in history.
Quickly navigate in command history
The function c shows the command history as enumerated list similarly to
the d function. Selections are also paste into the X clipboard. It's possible
to load a command of a former prompt by giving the prompt line number as
argument.
Bookmarks
A bookmark can be created with mark. It can be removed with unmark.
Bookmarks are universal and thus persistant.
A new shell automatically changes working directory on startup to newest bookmark.
m is a function that shows the bookmarks as enumerated list equivalently to d.
The following shortcuts need vi mode:
- Create a bookmark for present working directory with
min NORMAL mode. - Remove a bookmark for present working directory with
Min NORMAL mode.
Edit commandline with your favorite editor
The function edit-commandline let you edit the commandline with your editor.
It makes the commandline as powerful as your editor. If $EDITOR is not set,
vi is used.
The following shortcut needs vi mode:
- Type
.in NORMAL mode or\cvin NORMAL/INSERT mode to edit commandline in editor.
Sessions
Shell session can be stored with s <session name>. If a session with session name already exists, the session with this name will be attached. If a session with
session name is already active within another terminal, this terminal will be
focussed.
A list of available sessions can be shown with s.
A session can be erased with s -e <session name>.
Type s -d to detach current session.
Set window title
Just type wt <title>.
TODO
- vi REPLACE mode, as soon as REPLACE mode is implemented within fish