[](https://godoc.org/github.com/emirpasic/gods)
[](https://circleci.com/gh/emirpasic/gods?branch=master)
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/emirpasic/gods)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/emirpasic/gods)
[](https://sourcegraph.com/github.com/emirpasic/gods?badge)
[](https://github.com/emirpasic/gods/releases)
[](https://sonarcloud.io/summary/new_code?id=gods)
[](https://github.com/emirpasic/gods/blob/master/LICENSE)
# GoDS (Go Data Structures)
Implementation of various data structures and algorithms in Go.
## Data Structures
- [Containers](#containers)
- [Lists](#lists)
- [ArrayList](#arraylist)
- [SinglyLinkedList](#singlylinkedlist)
- [DoublyLinkedList](#doublylinkedlist)
- [Sets](#sets)
- [HashSet](#hashset)
- [TreeSet](#treeset)
- [LinkedHashSet](#linkedhashset)
- [Stacks](#stacks)
- [LinkedListStack](#linkedliststack)
- [ArrayStack](#arraystack)
- [Maps](#maps)
- [HashMap](#hashmap)
- [TreeMap](#treemap)
- [LinkedHashMap](#linkedhashmap)
- [HashBidiMap](#hashbidimap)
- [TreeBidiMap](#treebidimap)
- [Trees](#trees)
- [RedBlackTree](#redblacktree)
- [AVLTree](#avltree)
- [BTree](#btree)
- [BinaryHeap](#binaryheap)
- [Queues](#queues)
- [LinkedListQueue](#linkedlistqueue)
- [ArrayQueue](#arrayqueue)
- [CircularBuffer](#circularbuffer)
- [PriorityQueue](#priorityqueue)
- [Functions](#functions)
- [Comparator](#comparator)
- [Iterator](#iterator)
- [IteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex)
- [IteratorWithKey](#iteratorwithkey)
- [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex)
- [ReverseIteratorWithKey](#reverseiteratorwithkey)
- [Enumerable](#enumerable)
- [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex)
- [EnumerableWithKey](#enumerablewithkey)
- [Serialization](#serialization)
- [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer)
- [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer)
- [Sort](#sort)
- [Container](#container)
- [Appendix](#appendix)
## Containers
All data structures implement the container interface with the following methods:
```go
type Container interface {
Empty() bool
Size() int
Clear()
Values() []interface{}
String() string
}
```
Containers are either ordered or unordered. All ordered containers provide [stateful iterators](#iterator) and some of them allow [enumerable functions](#enumerable).
| **Data** | **Structure** | **Ordered** | **[Iterator](#iterator)** | **[Enumerable](#enumerable)** | **Referenced by** |
| :--- |:--------------------------------------| :---: | :---: | :---: | :---: |
| [Lists](#lists) |
| | [ArrayList](#arraylist) | yes | yes* | yes | index |
| | [SinglyLinkedList](#singlylinkedlist) | yes | yes | yes | index |
| | [DoublyLinkedList](#doublylinkedlist) | yes | yes* | yes | index |
| [Sets](#sets) |
| | [HashSet](#hashset) | no | no | no | index |
| | [TreeSet](#treeset) | yes | yes* | yes | index |
| | [LinkedHashSet](#linkedhashset) | yes | yes* | yes | index |
| [Stacks](#stacks) |
| | [LinkedListStack](#linkedliststack) | yes | yes | no | index |
| | [ArrayStack](#arraystack) | yes | yes* | no | index |
| [Maps](#maps) |
| | [HashMap](#hashmap) | no | no | no | key |
| | [TreeMap](#treemap) | yes | yes* | yes | key |
| | [LinkedHashMap](#linkedhashmap) | yes | yes* | yes | key |
| | [HashBidiMap](#hashbidimap) | no | no | no | key* |
| | [TreeBidiMap](#treebidimap) | yes | yes* | yes | key* |
| [Trees](#trees) |
| | [RedBlackTree](#redblacktree) | yes | yes* | no | key |
| | [AVLTree](#avltree) | yes | yes* | no | key |
| | [BTree](#btree) | yes | yes* | no | key |
| | [BinaryHeap](#binaryheap) | yes | yes* | no | index |
| [Queues](#queues) |
| | [LinkedListQueue](#linkedlistqueue) | yes | yes | no | index |
| | [ArrayQueue](#arrayqueue) | yes | yes* | no | index |
| | [CircularBuffer](#circularbuffer) | yes | yes* | no | index |
| | [PriorityQueue](#priorityqueue) | yes | yes* | no | index |
| | | | *reversible | | *bidirectional |
### Lists
A list is a data structure that stores values and may have repeated values.
Implements [Container](#containers) interface.
```go
type List interface {
Get(index int) (interface{}, bool)
Remove(index int)
Add(values ...interface{})
Contains(values ...interface{}) bool
Sort(comparator utils.Comparator)
Swap(index1, index2 int)
Insert(index int, values ...interface{})
Set(index int, value interface{})
containers.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
// String() string
}
```
#### ArrayList
A [list](#lists) backed by a dynamic array that grows and shrinks implicitly.
Implements [List](#lists), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import (
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/lists/arraylist"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
func main() {
list := arraylist.New()
list.Add("a") // ["a"]
list.Add("c", "b") // ["a","c","b"]
list.Sort(utils.StringComparator) // ["a","b","c"]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // "a",true
_, _ = list.Get(100) // nil,false
_ = list.Contains("a", "b", "c") // true
_ = list.Contains("a", "b", "c", "d") // false
list.Swap(0, 1) // ["b","a",c"]
list.Remove(2) // ["b","a"]
list.Remove(1) // ["b"]
list.Remove(0) // []
list.Remove(0) // [] (ignored)
_ = list.Empty() // true
_ = list.Size() // 0
list.Add("a") // ["a"]
list.Clear() // []
list.Insert(0, "b") // ["b"]
list.Insert(0, "a") // ["a","b"]
}
```
#### SinglyLinkedList
A [list](#lists) where each element points to the next element in the list.
Implements [List](#lists), [IteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import (
sll "github.com/emirpasic/gods/lists/singlylinkedlist"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
func main() {
list := sll.New()
list.Add("a") // ["a"]
list.Add("c", "b") // ["a","c","b"]
list.Sort(utils.StringComparator) // ["a","b","c"]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // "a",true
_, _ = list.Get(100) // nil,false
_ = list.Contains("a", "b", "c") // true
_ = list.Contains("a", "b", "c", "d") // false
list.Swap(0, 1) // ["b","a",c"]
list.Remove(2) // ["b","a"]
list.Remove(1) // ["b"]
list.Remove(0) // []
list.Remove(0) // [] (ignored)
_ = list.Empty() // true
_ = list.Size() // 0
list.Add("a") // ["a"]
list.Clear() // []
list.Insert(0, "b") // ["b"]
list.Insert(0, "a") // ["a","b"]
}
```
#### DoublyLinkedList
A [list](#lists) where each element points to the next and previous elements in the list.
Implements [List](#lists), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import (
dll "github.com/emirpasic/gods/lists/doublylinkedlist"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
func main() {
list := dll.New()
list.Add("a") // ["a"]
list.Add("c", "b") // ["a","c","b"]
list.Sort(utils.StringComparator) // ["a","b","c"]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // "a",true
_, _ = list.Get(100) // nil,false
_ = list.Contains("a", "b", "c") // true
_ = list.Contains("a", "b", "c", "d") // false
list.Swap(0, 1) // ["b","a",c"]
list.Remove(2) // ["b","a"]
list.Remove(1) // ["b"]
list.Remove(0) // []
list.Remove(0) // [] (ignored)
_ = list.Empty() // true
_ = list.Size() // 0
list.Add("a") // ["a"]
list.Clear() // []
list.Insert(0, "b") // ["b"]
list.Insert(0, "a") // ["a","b"]
}
```
### Sets
A set is a data structure that can store elements and has no repeated values. It is a computer implementation of the mathematical concept of a finite set. Unlike most other collection types, rather than retrieving a specific element from a set, one typically tests an element for membership in a set. This structure is often used to ensure that no duplicates are present in a container.
Set additionally allow set operations such as [intersection](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intersection_(set_theory)), [union](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Union_(set_theory)), [difference](https://proofwiki.org/wiki/Definition:Set_Difference), etc.
Implements [Container](#containers) interface.
```go
type Set interface {
Add(elements ...interface{})
Remove(elements ...interface{})
Contains(elements ...interface{}) bool
// Intersection(another *Set) *Set
// Union(another *Set) *Set
// Difference(another *Set) *Set
containers.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
// String() string
}
```
#### HashSet
A [set](#sets) backed by a hash table (actually a Go's map). It makes no guarantees as to the iteration order of the set.
Implements [Set](#sets), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/sets/hashset"
func main() {
set := hashset.New() // empty
set.Add(1) // 1
set.Add(2, 2, 3, 4, 5) // 3, 1, 2, 4, 5 (random order, duplicates ignored)
set.Remove(4) // 5, 3, 2, 1 (random order)
set.Remove(2, 3) // 1, 5 (random order)
set.Contains(1) // true
set.Contains(1, 5) // true
set.Contains(1, 6) // false
_ = set.Values() // []int{5,1} (random order)
set.Clear() // empty
set.Empty() // true
set.Size() // 0
}
```
#### TreeSet
A [set](#sets) backed by a [red-black tree](#redblacktree) to keep the elements ordered with respect to the [comparator](#comparator).
Implements [Set](#sets), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/sets/treeset"
func main() {
set := treeset.NewWithIntComparator() // empty (keys are of type int)
set.Add(1) // 1
set.Add(2, 2, 3, 4, 5) // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (in order, duplicates ignored)
set.Remove(4) // 1, 2, 3, 5 (in order)
set.Remove(2, 3) // 1, 5 (in order)
set.Contains(1) // true
set.Contains(1, 5) // true
set.Contains(1, 6) // false
_ = set.Values() // []int{1,5} (in order)
set.Clear() // empty
set.Empty() // true
set.Size() // 0
}
```
#### LinkedHashSet
A [set](#sets) that preserves insertion-order. Data structure is backed by a hash table to store values and [doubly-linked list](#doublylinkedlist) to store insertion ordering.
Implements [Set](#sets), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/sets/linkedhashset"
func main() {
set := linkedhashset.New() // empty
set.Add(5) // 5
set.Add(4, 4, 3, 2, 1) // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 (in insertion-order, duplicates ignored)
set.Add(4) // 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 (duplicates ignored, insertion-order unchanged)
set.Remove(4) // 5, 3, 2, 1 (in insertion-order)
set.Remove(2, 3) // 5, 1 (in insertion-order)
set.Contains(1) // true
set.Contains(1, 5) // true
set.Contains(1, 6) // false
_ = set.Values() // []int{5, 1} (in insertion-order)
set.Clear() // empty
set.Empty() // true
set.Size() // 0
}
```
### Stacks
A stack that represents a last-in-first-out (LIFO) data structure. The usual push and pop operations are provided, as well as a method to peek at the top item on the stack.
Implements [Container](#containers) interface.
```go
type Stack interface {
Push(value interface{})
Pop() (value interface{}, ok bool)
Peek() (value interface{}, ok bool)
containers.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
// String() string
}
```
#### LinkedListStack
A [stack](#stacks) based on a [linked list](#singlylinkedlist).
Implements [Stack](#stacks), [IteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import lls "github.com/emirpasic/gods/stacks/linkedliststack"
func main() {
stack := lls.New() // empty
stack.Push(1) // 1
stack.Push(2) // 1, 2
stack.Values() // 2, 1 (LIFO order)
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 2,true
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 2, true
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 1, true
_, _ = stack.Pop() // nil, false (nothing to pop)
stack.Push(1) // 1
stack.Clear() // empty
stack.Empty() // true
stack.Size() // 0
}
```
#### ArrayStack
A [stack](#stacks) based on a [array list](#arraylist).
Implements [Stack](#stacks), [IteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/stacks/arraystack"
func main() {
stack := arraystack.New() // empty
stack.Push(1) // 1
stack.Push(2) // 1, 2
stack.Values() // 2, 1 (LIFO order)
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 2,true
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 2, true
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 1, true
_, _ = stack.Pop() // nil, false (nothing to pop)
stack.Push(1) // 1
stack.Clear() // empty
stack.Empty() // true
stack.Size() // 0
}
```
### Maps
A Map is a data structure that maps keys to values. A map cannot contain duplicate keys and each key can map to at most one value.
Implements [Container](#containers) interface.
```go
type Map interface {
Put(key interface{}, value interface{})
Get(key interface{}) (value interface{}, found bool)
Remove(key interface{})
Keys() []interface{}
containers.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
// String() string
}
```
A BidiMap is an extension to the Map. A bidirectional map (BidiMap), also called a hash bag, is an associative data structure in which the key-value pairs form a one-to-one relation. This relation works in both directions by allow the value to also act as a key to key, e.g. a pair (a,b) thus provides a coupling between 'a' and 'b' so that 'b' can be found when 'a' is used as a key and 'a' can be found when 'b' is used as a key.
```go
type BidiMap interface {
GetKey(value interface{}) (key interface{}, found bool)
Map
}
```
#### HashMap
A [map](#maps) based on hash tables. Keys are unordered.
Implements [Map](#maps), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/hashmap"
func main() {
m := hashmap.New() // empty
m.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
m.Put(2, "b") // 2->b, 1->x (random order)
m.Put(1, "a") // 2->b, 1->a (random order)
_, _ = m.Get(2) // b, true
_, _ = m.Get(3) // nil, false
_ = m.Values() // []interface {}{"b", "a"} (random order)
_ = m.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2} (random order)
m.Remove(1) // 2->b
m.Clear() // empty
m.Empty() // true
m.Size() // 0
}
```
#### TreeMap
A [map](#maps) based on [red-black tree](#redblacktree). Keys are ordered with respect to the [comparator](#comparator).
Implements [Map](#maps), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithKey](#enumerablewithkey), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/treemap"
func main() {
m := treemap.NewWithIntComparator() // empty (keys are of type int)
m.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
m.Put(2, "b") // 1->x, 2->b (in order)
m.Put(1, "a") // 1->a, 2->b (in order)
_, _ = m.Get(2) // b, true
_, _ = m.Get(3) // nil, false
_ = m.Values() // []interface {}{"a", "b"} (in order)
_ = m.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2} (in order)
m.Remove(1) // 2->b
m.Clear() // empty
m.Empty() // true
m.Size() // 0
// Other:
m.Min() // Returns the minimum key and its value from map.
m.Max() // Returns the maximum key and its value from map.
}
```
#### LinkedHashMap
A [map](#maps) that preserves insertion-order. It is backed by a hash table to store values and [doubly-linked list](doublylinkedlist) to store ordering.
Implements [Map](#maps), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithKey](#enumerablewithkey), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/linkedhashmap"
func main() {
m := linkedhashmap.New() // empty (keys are of type int)
m.Put(2, "b") // 2->b
m.Put(1, "x") // 2->b, 1->x (insertion-order)
m.Put(1, "a") // 2->b, 1->a (insertion-order)
_, _ = m.Get(2) // b, true
_, _ = m.Get(3) // nil, false
_ = m.Values() // []interface {}{"b", "a"} (insertion-order)
_ = m.Keys() // []interface {}{2, 1} (insertion-order)
m.Remove(1) // 2->b
m.Clear() // empty
m.Empty() // true
m.Size() // 0
}
```
#### HashBidiMap
A [map](#maps) based on two hashmaps. Keys are unordered.
Implements [BidiMap](#maps), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/hashbidimap"
func main() {
m := hashbidimap.New() // empty
m.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
m.Put(3, "b") // 1->x, 3->b (random order)
m.Put(1, "a") // 1->a, 3->b (random order)
m.Put(2, "b") // 1->a, 2->b (random order)
_, _ = m.GetKey("a") // 1, true
_, _ = m.Get(2) // b, true
_, _ = m.Get(3) // nil, false
_ = m.Values() // []interface {}{"a", "b"} (random order)
_ = m.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2} (random order)
m.Remove(1) // 2->b
m.Clear() // empty
m.Empty() // true
m.Size() // 0
}
```
#### TreeBidiMap
A [map](#maps) based on red-black tree. This map guarantees that the map will be in both ascending key and value order. Other than key and value ordering, the goal with this structure is to avoid duplication of elements (unlike in [HashBidiMap](#hashbidimap)), which can be significant if contained elements are large.
Implements [BidiMap](#maps), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [EnumerableWithKey](#enumerablewithkey), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import (
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/treebidimap"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
func main() {
m := treebidimap.NewWith(utils.IntComparator, utils.StringComparator)
m.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
m.Put(3, "b") // 1->x, 3->b (ordered)
m.Put(1, "a") // 1->a, 3->b (ordered)
m.Put(2, "b") // 1->a, 2->b (ordered)
_, _ = m.GetKey("a") // 1, true
_, _ = m.Get(2) // b, true
_, _ = m.Get(3) // nil, false
_ = m.Values() // []interface {}{"a", "b"} (ordered)
_ = m.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2} (ordered)
m.Remove(1) // 2->b
m.Clear() // empty
m.Empty() // true
m.Size() // 0
}
```
### Trees
A tree is a widely used data data structure that simulates a hierarchical tree structure, with a root value and subtrees of children, represented as a set of linked nodes; thus no cyclic links.
Implements [Container](#containers) interface.
```go
type Tree interface {
containers.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
// String() string
}
```
#### RedBlackTree
A red–black [tree](#trees) is a binary search tree with an extra bit of data per node, its color, which can be either red or black. The extra bit of storage ensures an approximately balanced tree by constraining how nodes are colored from any path from the root to the leaf. Thus, it is a data structure which is a type of self-balancing binary search tree.
The balancing of the tree is not perfect but it is good enough to allow it to guarantee searching in O(log n) time, where n is the total number of elements in the tree. The insertion and deletion operations, along with the tree rearrangement and recoloring, are also performed in O(log n) time. [Wikipedia](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red%E2%80%93black_tree)
Implements [Tree](#trees), [ReverseIteratorWithKey](#reverseiteratorwithkey), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.

```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
rbt "github.com/emirpasic/gods/trees/redblacktree"
)
func main() {
tree := rbt.NewWithIntComparator() // empty (keys are of type int)
tree.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
tree.Put(2, "b") // 1->x, 2->b (in order)
tree.Put(1, "a") // 1->a, 2->b (in order, replacement)
tree.Put(3, "c") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c (in order)
tree.Put(4, "d") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d (in order)
tree.Put(5, "e") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e (in order)
tree.Put(6, "f") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f (in order)
fmt.Println(tree)
//
// RedBlackTree
// │ ┌── 6
// │ ┌── 5
// │ ┌── 4
// │ │ └── 3
// └── 2
// └── 1
_ = tree.Values() // []interface {}{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"} (in order)
_ = tree.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} (in order)
tree.Remove(2) // 1->a, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f (in order)
fmt.Println(tree)
//
// RedBlackTree
// │ ┌── 6
// │ ┌── 5
// └── 4
// │ ┌── 3
// └── 1
tree.Clear() // empty
tree.Empty() // true
tree.Size() // 0
// Other:
tree.Left() // gets the left-most (min) node
tree.Right() // get the right-most (max) node
tree.Floor(1) // get the floor node
tree.Ceiling(1) // get the ceiling node
}
```
Extending the red-black tree's functionality has been demonstrated in the following [example](https://github.com/emirpasic/gods/blob/master/examples/redblacktreeextended/redblacktreeextended.go).
#### AVLTree
AVL [tree](#trees) is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Lookup, insertion, and deletion all take O(log n) time in both the average and worst cases, where n is the number of nodes in the tree prior to the operation. Insertions and deletions may require the tree to be rebalanced by one or more tree rotations.
AVL trees are often compared with red–black trees because both support the same set of operations and take O(log n) time for the basic operations. For lookup-intensive applications, AVL trees are faster than red–black trees because they are more strictly balanced. [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AVL_tree)
Implements [Tree](#trees), [ReverseIteratorWithKey](#reverseiteratorwithkey), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
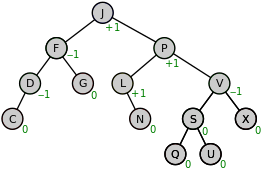
AVL tree with balance factors (green)
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
avl "github.com/emirpasic/gods/trees/avltree"
)
func main() {
tree := avl.NewWithIntComparator() // empty(keys are of type int)
tree.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
tree.Put(2, "b") // 1->x, 2->b (in order)
tree.Put(1, "a") // 1->a, 2->b (in order, replacement)
tree.Put(3, "c") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c (in order)
tree.Put(4, "d") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d (in order)
tree.Put(5, "e") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e (in order)
tree.Put(6, "f") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f (in order)
fmt.Println(tree)
//
// AVLTree
// │ ┌── 6
// │ ┌── 5
// └── 4
// │ ┌── 3
// └── 2
// └── 1
_ = tree.Values() // []interface {}{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"} (in order)
_ = tree.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} (in order)
tree.Remove(2) // 1->a, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f (in order)
fmt.Println(tree)
//
// AVLTree
// │ ┌── 6
// │ ┌── 5
// └── 4
// └── 3
// └── 1
tree.Clear() // empty
tree.Empty() // true
tree.Size() // 0
}
```
#### BTree
B-tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two children.
According to Knuth's definition, a B-tree of order m is a tree which satisfies the following properties:
- Every node has at most m children.
- Every non-leaf node (except root) has at least ⌈m/2⌉ children.
- The root has at least two children if it is not a leaf node.
- A non-leaf node with k children contains k−1 keys.
- All leaves appear in the same level
Each internal node’s keys act as separation values which divide its subtrees. For example, if an internal node has 3 child nodes (or subtrees) then it must have 2 keys: a1 and a2. All values in the leftmost subtree will be less than a1, all values in the middle subtree will be between a1 and a2, and all values in the rightmost subtree will be greater than a2.[Wikipedia](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red%E2%80%93black_tree)
Implements [Tree](#trees), [ReverseIteratorWithKey](#reverseiteratorwithkey), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.

```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/trees/btree"
)
func main() {
tree := btree.NewWithIntComparator(3) // empty (keys are of type int)
tree.Put(1, "x") // 1->x
tree.Put(2, "b") // 1->x, 2->b (in order)
tree.Put(1, "a") // 1->a, 2->b (in order, replacement)
tree.Put(3, "c") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c (in order)
tree.Put(4, "d") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d (in order)
tree.Put(5, "e") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e (in order)
tree.Put(6, "f") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f (in order)
tree.Put(7, "g") // 1->a, 2->b, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f, 7->g (in order)
fmt.Println(tree)
// BTree
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// 5
// 6
// 7
_ = tree.Values() // []interface {}{"a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g"} (in order)
_ = tree.Keys() // []interface {}{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7} (in order)
tree.Remove(2) // 1->a, 3->c, 4->d, 5->e, 6->f, 7->g (in order)
fmt.Println(tree)
// BTree
// 1
// 3
// 4
// 5
// 6
// 7
tree.Clear() // empty
tree.Empty() // true
tree.Size() // 0
// Other:
tree.Height() // gets the height of the tree
tree.Left() // gets the left-most (min) node
tree.LeftKey() // get the left-most (min) node's key
tree.LeftValue() // get the left-most (min) node's value
tree.Right() // get the right-most (max) node
tree.RightKey() // get the right-most (max) node's key
tree.RightValue() // get the right-most (max) node's value
}
```
#### BinaryHeap
A binary heap is a [tree](#trees) created using a binary tree. It can be seen as a binary tree with two additional constraints:
- Shape property:
A binary heap is a complete binary tree; that is, all levels of the tree, except possibly the last one (deepest) are fully filled, and, if the last level of the tree is not complete, the nodes of that level are filled from left to right.
- Heap property:
All nodes are either greater than or equal to or less than or equal to each of its children, according to a comparison predicate defined for the heap. [Wikipedia](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_heap)
Implements [Tree](#trees), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#reverseiteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.

```go
package main
import (
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/trees/binaryheap"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
func main() {
// Min-heap
heap := binaryheap.NewWithIntComparator() // empty (min-heap)
heap.Push(2) // 2
heap.Push(3) // 2, 3
heap.Push(1) // 1, 3, 2
heap.Values() // 1, 3, 2
_, _ = heap.Peek() // 1,true
_, _ = heap.Pop() // 1, true
_, _ = heap.Pop() // 2, true
_, _ = heap.Pop() // 3, true
_, _ = heap.Pop() // nil, false (nothing to pop)
heap.Push(1) // 1
heap.Clear() // empty
heap.Empty() // true
heap.Size() // 0
// Max-heap
inverseIntComparator := func(a, b interface{}) int {
return -utils.IntComparator(a, b)
}
heap = binaryheap.NewWith(inverseIntComparator) // empty (min-heap)
heap.Push(2, 3, 1) // 3, 2, 1 (bulk optimized)
heap.Values() // 3, 2, 1
}
```
### Queues
A queue that represents a first-in-first-out (FIFO) data structure. The usual enqueue and dequeue operations are provided, as well as a method to peek at the first item in the queue.
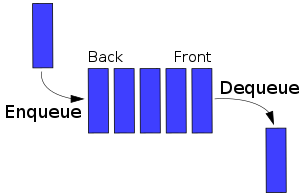
Implements [Container](#containers) interface.
```go
type Queue interface {
Enqueue(value interface{})
Dequeue() (value interface{}, ok bool)
Peek() (value interface{}, ok bool)
containers.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
// String() string
}
```
#### LinkedListQueue
A [queue](#queues) based on a [linked list](#singlylinkedlist).
Implements [Queue](#queues), [IteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import llq "github.com/emirpasic/gods/queues/linkedlistqueue"
// LinkedListQueueExample to demonstrate basic usage of LinkedListQueue
func main() {
queue := llq.New() // empty
queue.Enqueue(1) // 1
queue.Enqueue(2) // 1, 2
_ = queue.Values() // 1, 2 (FIFO order)
_, _ = queue.Peek() // 1,true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 1, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 2, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // nil, false (nothing to deque)
queue.Enqueue(1) // 1
queue.Clear() // empty
queue.Empty() // true
_ = queue.Size() // 0
}
```
#### ArrayQueue
A [queue](#queues) based on a [array list](#arraylist).
Implements [Queue](#queues), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import aq "github.com/emirpasic/gods/queues/arrayqueue"
// ArrayQueueExample to demonstrate basic usage of ArrayQueue
func main() {
queue := aq.New() // empty
queue.Enqueue(1) // 1
queue.Enqueue(2) // 1, 2
_ = queue.Values() // 1, 2 (FIFO order)
_, _ = queue.Peek() // 1,true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 1, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 2, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // nil, false (nothing to deque)
queue.Enqueue(1) // 1
queue.Clear() // empty
queue.Empty() // true
_ = queue.Size() // 0
}
```
#### CircularBuffer
A circular buffer, circular [queue](#queues), cyclic buffer or ring buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed-size buffer as if it were connected end-to-end. This structure lends itself easily to buffering data streams.

Implements [Queue](#queues), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import cb "github.com/emirpasic/gods/queues/circularbuffer"
// CircularBufferExample to demonstrate basic usage of CircularBuffer
func main() {
queue := cb.New(3) // empty (max size is 3)
queue.Enqueue(1) // 1
queue.Enqueue(2) // 1, 2
queue.Enqueue(3) // 1, 2, 3
_ = queue.Values() // 1, 2, 3
queue.Enqueue(3) // 4, 2, 3
_, _ = queue.Peek() // 4,true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 4, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 2, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // 3, true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // nil, false (nothing to deque)
queue.Enqueue(1) // 1
queue.Clear() // empty
queue.Empty() // true
_ = queue.Size() // 0
}
```
#### PriorityQueue
A priority queue is a special type of [queue](#queues) in which each element is associated with a priority value. And, elements are served on the basis of their priority. That is, higher priority elements are served first. However, if elements with the same priority occur, they are served according to their order in the queue.
Implements [Queue](#queues), [ReverseIteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), [JSONSerializer](#jsonserializer) and [JSONDeserializer](#jsondeserializer) interfaces.
```go
package main
import (
pq "github.com/emirpasic/gods/queues/priorityqueue"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
// Element is an entry in the priority queue
type Element struct {
name string
priority int
}
// Comparator function (sort by element's priority value in descending order)
func byPriority(a, b interface{}) int {
priorityA := a.(Element).priority
priorityB := b.(Element).priority
return -utils.IntComparator(priorityA, priorityB) // "-" descending order
}
// PriorityQueueExample to demonstrate basic usage of BinaryHeap
func main() {
a := Element{name: "a", priority: 1}
b := Element{name: "b", priority: 2}
c := Element{name: "c", priority: 3}
queue := pq.NewWith(byPriority) // empty
queue.Enqueue(a) // {a 1}
queue.Enqueue(c) // {c 3}, {a 1}
queue.Enqueue(b) // {c 3}, {b 2}, {a 1}
_ = queue.Values() // [{c 3} {b 2} {a 1}]
_, _ = queue.Peek() // {c 3} true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // {c 3} true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // {b 2} true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // {a 1} true
_, _ = queue.Dequeue() // false (nothing to dequeue)
queue.Clear() // empty
_ = queue.Empty() // true
_ = queue.Size() // 0
}
```
## Functions
Various helper functions used throughout the library.
### Comparator
Some data structures (e.g. TreeMap, TreeSet) require a comparator function to automatically keep their elements sorted upon insertion. This comparator is necessary during the initalization.
Comparator is defined as:
Return values (int):
```go
negative , if a < b
zero , if a == b
positive , if a > b
```
Comparator signature:
```go
type Comparator func(a, b interface{}) int
```
All common comparators for builtin types are included in the library:
```go
func StringComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func IntComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int8Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int16Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UIntComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt8Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt16Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Float32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Float64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func ByteComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func RuneComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func TimeComparator(a, b interface{}) int
```
Writing custom comparators is easy:
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/sets/treeset"
)
type User struct {
id int
name string
}
// Custom comparator (sort by IDs)
func byID(a, b interface{}) int {
// Type assertion, program will panic if this is not respected
c1 := a.(User)
c2 := b.(User)
switch {
case c1.id > c2.id:
return 1
case c1.id < c2.id:
return -1
default:
return 0
}
}
func main() {
set := treeset.NewWith(byID)
set.Add(User{2, "Second"})
set.Add(User{3, "Third"})
set.Add(User{1, "First"})
set.Add(User{4, "Fourth"})
fmt.Println(set) // {1 First}, {2 Second}, {3 Third}, {4 Fourth}
}
```
### Iterator
All ordered containers have stateful iterators. Typically an iterator is obtained by _Iterator()_ function of an ordered container. Once obtained, iterator's _Next()_ function moves the iterator to the next element and returns true if there was a next element. If there was an element, then element's can be obtained by iterator's _Value()_ function. Depending on the ordering type, it's position can be obtained by iterator's _Index()_ or _Key()_ functions. Some containers even provide reversible iterators, essentially the same, but provide another extra _Prev()_ function that moves the iterator to the previous element and returns true if there was a previous element.
Note: it is unsafe to remove elements from container while iterating.
#### IteratorWithIndex
An [iterator](#iterator) whose elements are referenced by an index.
Typical usage:
```go
it := list.Iterator()
for it.Next() {
index, value := it.Index(), it.Value()
...
}
```
Other usages:
```go
if it.First() {
firstIndex, firstValue := it.Index(), it.Value()
...
}
```
```go
for it.Begin(); it.Next(); {
...
}
```
Seeking to a specific element:
```go
// Seek function, i.e. find element starting with "b"
seek := func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return strings.HasSuffix(value.(string), "b")
}
// Seek to the condition and continue traversal from that point (forward).
// assumes it.Begin() was called.
for found := it.NextTo(seek); found; found = it.Next() {
index, value := it.Index(), it.Value()
...
}
```
#### IteratorWithKey
An [iterator](#iterator) whose elements are referenced by a key.
Typical usage:
```go
it := tree.Iterator()
for it.Next() {
key, value := it.Key(), it.Value()
...
}
```
Other usages:
```go
if it.First() {
firstKey, firstValue := it.Key(), it.Value()
...
}
```
```go
for it.Begin(); it.Next(); {
...
}
```
Seeking to a specific element from the current iterator position:
```go
// Seek function, i.e. find element starting with "b"
seek := func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return strings.HasSuffix(value.(string), "b")
}
// Seek to the condition and continue traversal from that point (forward).
// assumes it.Begin() was called.
for found := it.NextTo(seek); found; found = it.Next() {
key, value := it.Key(), it.Value()
...
}
```
#### ReverseIteratorWithIndex
An [iterator](#iterator) whose elements are referenced by an index. Provides all functions as [IteratorWithIndex](#iteratorwithindex), but can also be used for reverse iteration.
Typical usage of iteration in reverse:
```go
it := list.Iterator()
for it.End(); it.Prev(); {
index, value := it.Index(), it.Value()
...
}
```
Other usages:
```go
if it.Last() {
lastIndex, lastValue := it.Index(), it.Value()
...
}
```
Seeking to a specific element:
```go
// Seek function, i.e. find element starting with "b"
seek := func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return strings.HasSuffix(value.(string), "b")
}
// Seek to the condition and continue traversal from that point (in reverse).
// assumes it.End() was called.
for found := it.PrevTo(seek); found; found = it.Prev() {
index, value := it.Index(), it.Value()
...
}
```
#### ReverseIteratorWithKey
An [iterator](#iterator) whose elements are referenced by a key. Provides all functions as [IteratorWithKey](#iteratorwithkey), but can also be used for reverse iteration.
Typical usage of iteration in reverse:
```go
it := tree.Iterator()
for it.End(); it.Prev(); {
key, value := it.Key(), it.Value()
...
}
```
Other usages:
```go
if it.Last() {
lastKey, lastValue := it.Key(), it.Value()
...
}
```
```go
// Seek function, i.e. find element starting with "b"
seek := func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return strings.HasSuffix(value.(string), "b")
}
// Seek to the condition and continue traversal from that point (in reverse).
// assumes it.End() was called.
for found := it.PrevTo(seek); found; found = it.Prev() {
key, value := it.Key(), it.Value()
...
}
```
### Enumerable
Enumerable functions for ordered containers that implement [EnumerableWithIndex](#enumerablewithindex) or [EnumerableWithKey](#enumerablewithkey) interfaces.
#### EnumerableWithIndex
[Enumerable](#enumerable) functions for ordered containers whose values can be fetched by an index.
**Each**
Calls the given function once for each element, passing that element's index and value.
```go
Each(func(index int, value interface{}))
```
**Map**
Invokes the given function once for each element and returns a container containing the values returned by the given function.
```go
Map(func(index int, value interface{}) interface{}) Container
```
**Select**
Returns a new container containing all elements for which the given function returns a true value.
```go
Select(func(index int, value interface{}) bool) Container
```
**Any**
Passes each element of the container to the given function and returns true if the function ever returns true for any element.
```go
Any(func(index int, value interface{}) bool) bool
```
**All**
Passes each element of the container to the given function and returns true if the function returns true for all elements.
```go
All(func(index int, value interface{}) bool) bool
```
**Find**
Passes each element of the container to the given function and returns the first (index,value) for which the function is true or -1,nil otherwise if no element matches the criteria.
```go
Find(func(index int, value interface{}) bool) (int, interface{})}
```
**Example:**
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/sets/treeset"
)
func printSet(txt string, set *treeset.Set) {
fmt.Print(txt, "[ ")
set.Each(func(index int, value interface{}) {
fmt.Print(value, " ")
})
fmt.Println("]")
}
func main() {
set := treeset.NewWithIntComparator()
set.Add(2, 3, 4, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8)
printSet("Initial", set) // [ 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ]
even := set.Select(func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int)%2 == 0
})
printSet("Even numbers", even) // [ 2 4 6 8 ]
foundIndex, foundValue := set.Find(func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int)%2 == 0 && value.(int)%3 == 0
})
if foundIndex != -1 {
fmt.Println("Number divisible by 2 and 3 found is", foundValue, "at index", foundIndex) // value: 6, index: 4
}
square := set.Map(func(index int, value interface{}) interface{} {
return value.(int) * value.(int)
})
printSet("Numbers squared", square) // [ 4 9 16 25 36 49 64 ]
bigger := set.Any(func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) > 5
})
fmt.Println("Set contains a number bigger than 5 is ", bigger) // true
positive := set.All(func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) > 0
})
fmt.Println("All numbers are positive is", positive) // true
evenNumbersSquared := set.Select(func(index int, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int)%2 == 0
}).Map(func(index int, value interface{}) interface{} {
return value.(int) * value.(int)
})
printSet("Chaining", evenNumbersSquared) // [ 4 16 36 64 ]
}
```
#### EnumerableWithKey
Enumerable functions for ordered containers whose values whose elements are key/value pairs.
**Each**
Calls the given function once for each element, passing that element's key and value.
```go
Each(func(key interface{}, value interface{}))
```
**Map**
Invokes the given function once for each element and returns a container containing the values returned by the given function as key/value pairs.
```go
Map(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) (interface{}, interface{})) Container
```
**Select**
Returns a new container containing all elements for which the given function returns a true value.
```go
Select(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool) Container
```
**Any**
Passes each element of the container to the given function and returns true if the function ever returns true for any element.
```go
Any(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool) bool
```
**All**
Passes each element of the container to the given function and returns true if the function returns true for all elements.
```go
All(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool) bool
```
**Find**
Passes each element of the container to the given function and returns the first (key,value) for which the function is true or nil,nil otherwise if no element matches the criteria.
```go
Find(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool) (interface{}, interface{})
```
**Example:**
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/treemap"
)
func printMap(txt string, m *treemap.Map) {
fmt.Print(txt, " { ")
m.Each(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) {
fmt.Print(key, ":", value, " ")
})
fmt.Println("}")
}
func main() {
m := treemap.NewWithStringComparator()
m.Put("g", 7)
m.Put("f", 6)
m.Put("e", 5)
m.Put("d", 4)
m.Put("c", 3)
m.Put("b", 2)
m.Put("a", 1)
printMap("Initial", m) // { a:1 b:2 c:3 d:4 e:5 f:6 g:7 }
even := m.Select(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) % 2 == 0
})
printMap("Elements with even values", even) // { b:2 d:4 f:6 }
foundKey, foundValue := m.Find(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) % 2 == 0 && value.(int) % 3 == 0
})
if foundKey != nil {
fmt.Println("Element with value divisible by 2 and 3 found is", foundValue, "with key", foundKey) // value: 6, index: 4
}
square := m.Map(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) (interface{}, interface{}) {
return key.(string) + key.(string), value.(int) * value.(int)
})
printMap("Elements' values squared and letters duplicated", square) // { aa:1 bb:4 cc:9 dd:16 ee:25 ff:36 gg:49 }
bigger := m.Any(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) > 5
})
fmt.Println("Map contains element whose value is bigger than 5 is", bigger) // true
positive := m.All(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) > 0
})
fmt.Println("All map's elements have positive values is", positive) // true
evenNumbersSquared := m.Select(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) bool {
return value.(int) % 2 == 0
}).Map(func(key interface{}, value interface{}) (interface{}, interface{}) {
return key, value.(int) * value.(int)
})
printMap("Chaining", evenNumbersSquared) // { b:4 d:16 f:36 }
}
```
### Serialization
All data structures can be serialized (marshalled) and deserialized (unmarshalled). Currently, only JSON support is available.
#### JSONSerializer
Outputs the container into its JSON representation.
Typical usage for key-value structures:
```go
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/hashmap"
)
func main() {
m := hashmap.New()
m.Put("a", "1")
m.Put("b", "2")
m.Put("c", "3")
bytes, err := json.Marshal(m) // Same as "m.ToJSON(m)"
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println(string(bytes)) // {"a":"1","b":"2","c":"3"}
}
```
Typical usage for value-only structures:
```go
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/lists/arraylist"
)
func main() {
list := arraylist.New()
list.Add("a", "b", "c")
bytes, err := json.Marshal(list) // Same as "list.ToJSON(list)"
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println(string(bytes)) // ["a","b","c"]
}
```
#### JSONDeserializer
Populates the container with elements from the input JSON representation.
Typical usage for key-value structures:
```go
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/maps/hashmap"
)
func main() {
hm := hashmap.New()
bytes := []byte(`{"a":"1","b":"2"}`)
err := json.Unmarshal(bytes, &hm) // Same as "hm.FromJSON(bytes)"
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println(hm) // HashMap map[b:2 a:1]
}
```
Typical usage for value-only structures:
```go
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/lists/arraylist"
)
func main() {
list := arraylist.New()
bytes := []byte(`["a","b"]`)
err := json.Unmarshal(bytes, &list) // Same as "list.FromJSON(bytes)"
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println(list) // ArrayList ["a","b"]
}
```
### Sort
Sort is a general purpose sort function.
Lists have an in-place _Sort()_ function and all containers can return their sorted elements via _containers.GetSortedValues()_ function.
Internally these all use the _utils.Sort()_ method:
```go
package main
import "github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
func main() {
strings := []interface{}{} // []
strings = append(strings, "d") // ["d"]
strings = append(strings, "a") // ["d","a"]
strings = append(strings, "b") // ["d","a",b"
strings = append(strings, "c") // ["d","a",b","c"]
utils.Sort(strings, utils.StringComparator) // ["a","b","c","d"]
}
```
### Container
Container specific operations:
```go
// Returns sorted container''s elements with respect to the passed comparator.
// Does not affect the ordering of elements within the container.
func GetSortedValues(container Container, comparator utils.Comparator) []interface{}
```
Usage:
```go
package main
import (
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/lists/arraylist"
"github.com/emirpasic/gods/utils"
)
func main() {
list := arraylist.New()
list.Add(2, 1, 3)
values := GetSortedValues(container, utils.StringComparator) // [1, 2, 3]
}
```
## Appendix
### Motivation
Collections and data structures found in other languages: Java Collections, C++ Standard Template Library (STL) containers, Qt Containers, Ruby Enumerable etc.
### Goals
**Fast algorithms**:
- Based on decades of knowledge and experiences of other libraries mentioned above.
**Memory efficient algorithms**:
- Avoiding to consume memory by using optimal algorithms and data structures for the given set of problems, e.g. red-black tree in case of TreeMap to avoid keeping redundant sorted array of keys in memory.
**Easy to use library**:
- Well-structured library with minimalistic set of atomic operations from which more complex operations can be crafted.
**Stable library**:
- Only additions are permitted keeping the library backward compatible.
**Solid documentation and examples**:
- Learning by example.
**Production ready**:
- Used in production.
**No dependencies**:
- No external imports.
There is often a tug of war between speed and memory when crafting algorithms. We choose to optimize for speed in most cases within reasonable limits on memory consumption.
Thread safety is not a concern of this project, this should be handled at a higher level.
### Testing and Benchmarking
This takes a while, so test within sub-packages:
`go test -run=NO_TEST -bench . -benchmem -benchtime 1s ./...`

### Contributing
Biggest contribution towards this library is to use it and give us feedback for further improvements and additions.
For direct contributions, _pull request_ into master branch or ask to become a contributor.
Coding style:
```shell
# Install tooling and set path:
go install gotest.tools/gotestsum@latest
go install golang.org/x/lint/golint@latest
go install github.com/kisielk/errcheck@latest
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
# Fix errors and warnings:
go fmt ./... &&
go test -v ./... &&
golint -set_exit_status ./... &&
! go fmt ./... 2>&1 | read &&
go vet -v ./... &&
gocyclo -avg -over 15 ../gods &&
errcheck ./...
```
### License
This library is distributed under the BSD-style license found in the [LICENSE](https://github.com/emirpasic/gods/blob/master/LICENSE) file.
### Sponsors
##  [BrowserStack](https://www.browserstack.com/?ref=webhook) is a cloud-based cross-browser testing tool that enables developers to test their websites across various browsers on different operating systems and mobile devices, without requiring users to install virtual machines, devices or emulators.
[BrowserStack](https://www.browserstack.com/?ref=webhook) is a cloud-based cross-browser testing tool that enables developers to test their websites across various browsers on different operating systems and mobile devices, without requiring users to install virtual machines, devices or emulators.







